What is Hyperkalemia?
Hyperkalemia is a condition that occurs when potassium levels in a person’s blood get too high. Potassium is an essential nutrient that is found in foods. This nutrient helps our nerves and muscles function. But excessive potassium in the blood can be dangerous. It can affect heart function and cause a heart attack. It is not easy to tell when the potassium levels are high.
What Causes Hyperkalemia?
There are some common causes that can lead to hyperkalemia. They are –
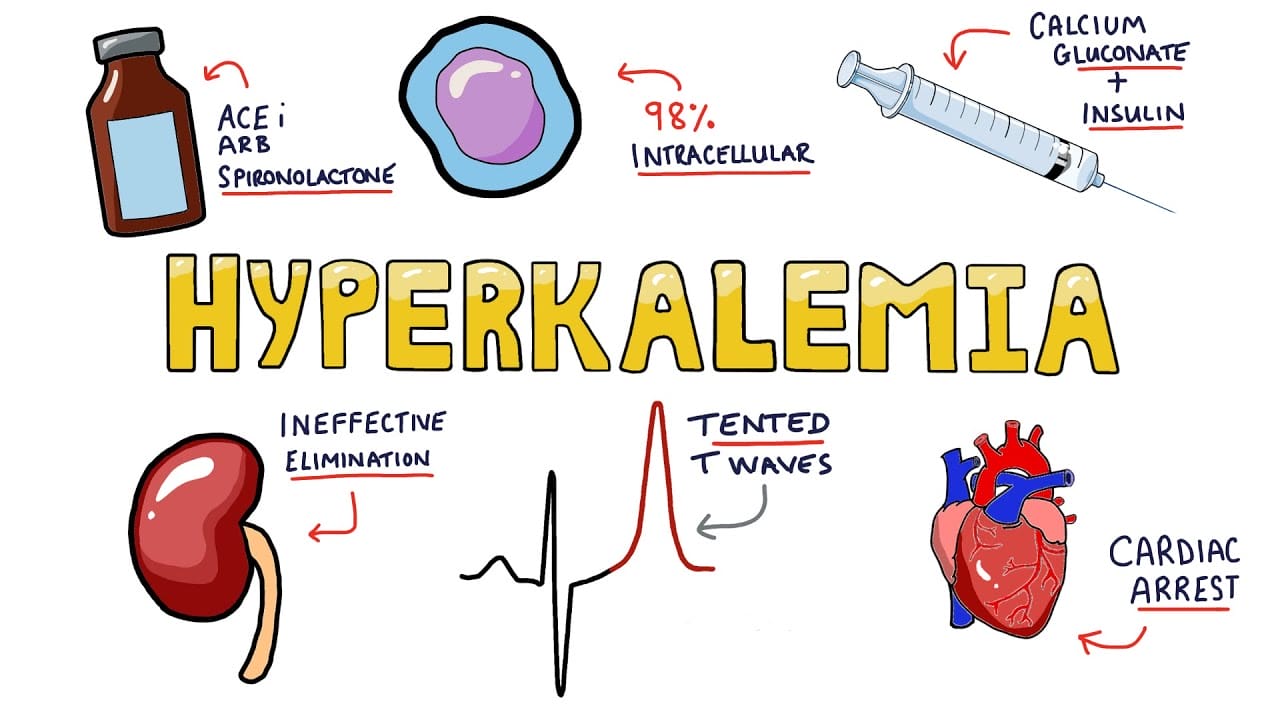
- Kidney disease: Hyperkalemia can be caused if the kidneys do not work well. Kidneys are responsible for balancing the amount of potassium intake and the amount lost through urine. Potassium is derived from the food that a person eats and the liquids they drink. It gets filtered by the kidneys and lost through the urine. When kidney disease is in its early stages, the kidneys can often make up for increased potassium. But as kidney function deteriorates, they may be unable to remove the excess potassium from the body.
- A high-potassium diet: Eating foods rich in potassium can majorly cause hyperkalemia, especially in people with advanced kidney disease. Foods that have a high potassium content are- cantaloupe, orange juice, and bananas.
- Drugs that prevent the kidneys from losing enough potassium: Some drugs can prevent the kidneys from removing enough potassium. This may cause the potassium levels to rise.

There are some other, less common causes of hyperkalemia. They are –
- Consuming extra potassium, though salt substitutes or supplements.
- ‘Addisons disease’ is a disorder that may occur if the body is not able to make enough of certain hormones. Hormones are basically chemicals that are produced by different glands and organs, including the kidneys to trigger certain responses in a person’s body.
- Burns or other severe injuries: The human body releases extra potassium in the blood in response to severe burns or injuries.
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Poorly controlled diabetes can have a direct effect on the kidneys that are responsible for balancing the potassium levels in an individual’s body.
Symptoms of Hyperkalemia
People with mild hyperkalemia usually have no signs in the initial stages. The symptoms may develop gradually over weeks or months. High potassium levels can become dangerous when they affect the heart and hint towards other life-threatening problems.
The symptoms in hyperkalemia include –
- Abdominal pain and diarrhea
- Chest pain
- Heart palpitations or arrhythmia
- Muscle weakness or numbness in limbs
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis of Hyperkalemia
Since most people do not have symptoms, they might not know they have high potassium until they get a routine blood test. A serum potassium test can measure the number of potassium levels in the blood. The doctor may also recommend an electrocardiogram. This test can show changes in the heart rhythm caused by hyperkalemia.
How is Hyperkalemia Treated?
The treatment for hyperkalemia may vary depending on the potassium level. The options of managing hyperkalemia include –
- Diuretics: These drugs are better known as water pills. They make a person suffering from hyperkalemia pee more often. The body gets rid of the excess potassium mainly through urine.
- Intravenous (IV) therapy: In extremely high potassium level cases, there is a need for immediate treatment. The doctor will provide an IV infusion of calcium to protect the patient’s heart. An infusion of insulin is then provided to help move potassium into the blood cells. A person may also require to inhale an asthma medication called albuterol that further lowers potassium levels.
- Medication management: The healthcare professional can determine what medication changes are required to bring out the best results. Many people see or notice improvement after stopping or regulating certain blood pressure medications and other drugs that increase potassium levels.
- Potassium binders: A daily medication helps bind excess potassium in the intestines. A person passes the potassium when they poop. The healthcare professional may recommend binders if no other treatment helps lower potassium levels.
- Dialysis: If the potassium levels continue to be high, or if they lead to kidney failure, one may need dialysis. Dialysis treatment can help the kidneys remove increased potassium from the blood.
The normal level of potassium in blood?
The level of potassium in a person’s blood should normally be between 3.5 and 5.0 millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
How to prevent hyperkalemia?
A person at the risk of hyperkalemia should protect their health through a low-potassium diet. One may need to limit or completely cut out their potassium intake. The foods that one should not consume in hyperkalemia include-
- Avocados
- Bananas
- Asparagus
- Oranges and grapefruit, and their juices
- Cooked spinach
- Potatoes
- Melons
- Prunes, raisins, and other dried fruits
- Pumpkin
- Salt substitutes having potassium in them
- Tomatoes and their products like ketchup and sauces
Treatment of hyperkalemia is often associated with the underlying cause. It becomes important for people with chronic kidney disease to get their potassium levels tested. The level of potassium in a person’s blood should normally be between 3.5 and 5.0 millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
Ayurveda mainly focuses on adopting steps like lifestyle modifications, monitoring diet, and ensuring enough rest.
Ayurveda helps reduce high potassium levels and can cure hyperkalemia. It treats the condition at a root level and does not have any side effects on the body. The ayurvedic treatment uses natural herbs and the procedure is therefore simple and hassle-free.
That is why high potassium reduction in Ayurveda is the best treatment alternative that a person can opt for to overcome hyperkalemia.

